The global focus on environmental conservation continues to grow, and businesses are increasingly aware of their impact on the planet. Supply chains, a major contributor to carbon emissions and waste, are under scrutiny as companies seek more eco-friendly solutions. Sustainability is no longer just a corporate buzzword; it’s a crucial strategy for long-term business success. This shift has led to the rise of circular supply chains, which prioritize efficiency and sustainability over the traditional linear model.
Table of Contents
Understanding Circular Supply Chains
A circular supply chain is designed to keep products, packaging, and materials in circulation for as long as possible. Instead of following a single-use path from production to disposal, circular models promote reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing. By reducing dependency on virgin materials and minimizing waste, businesses can lower costs and environmental impact.
Key principles of circular supply chains include:
- Designing products and packaging for longevity and recyclability.
- Reintegrating materials back into the production cycle.
- Utilizing reverse logistics to recover and reuse products.
- Reducing transportation inefficiencies to lower carbon footprints.
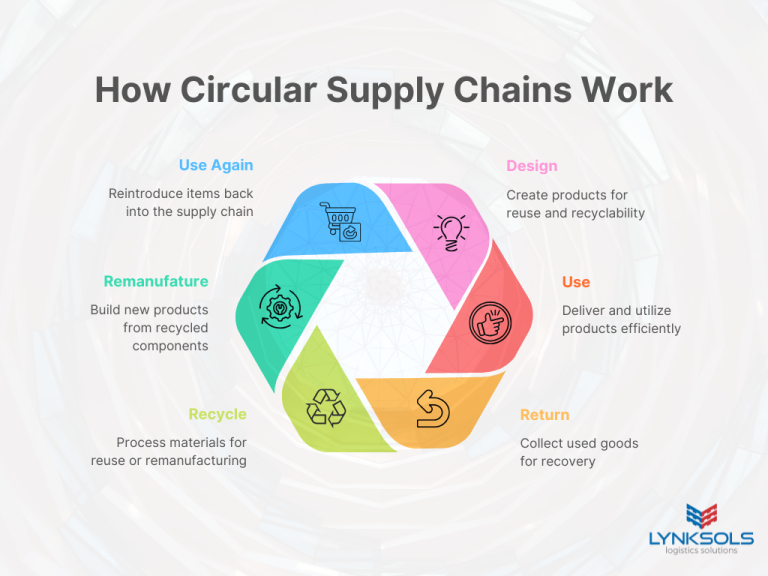
By adopting a circular approach, businesses can achieve long-term sustainability and resilience, ensuring they remain competitive in an evolving marketplace.
Why the Traditional Supply Chain Falls Short
Traditional supply chains follow a linear process: extract raw materials, manufacture products, distribute to consumers, and dispose of waste. While this model has driven economic growth for decades, it comes at a significant environmental cost. The reliance on finite resources, high energy consumption, and excessive waste generation have made it clear that linear supply chains are unsustainable in the long run.
Some of the major drawbacks of linear supply chains include:
- High material and disposal costs.
- Greater exposure to supply chain disruptions due to resource scarcity.
- Increased carbon emissions from production and transportation.
- Consumer pushback against unsustainable business practices.
Businesses that fail to transition toward sustainable models risk losing their competitive edge as regulations tighten and consumer preferences shift toward environmentally responsible companies.
How Circular Models Create Business Value
While transitioning to a circular supply chain requires investment and strategic planning, the long-term benefits outweigh the challenges. Companies that successfully integrate sustainability into their operations can expect:
- Cost Reduction – Minimizing raw material usage and reusing components can significantly cut expenses. Businesses can also reduce waste disposal costs by repurposing byproducts and packaging.
- Stronger Brand Reputation – Consumers are more likely to support brands that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. Adopting circular practices enhances corporate social responsibility (CSR) efforts and builds trust with stakeholders.
- Improved Supply Chain Resilience – Relying less on scarce resources and volatile markets allows businesses to maintain stable operations even during disruptions.
- Innovation and Competitive Advantage – Sustainable practices drive innovation in product design, materials, and logistics. Companies that invest in eco-friendly solutions differentiate themselves from competitors and future-proof their operations.
- Greater Operational Efficiency – A well-optimized circular supply chain reduces waste, shortens delivery times, and improves resource utilization, leading to leaner and more efficient processes.
Looking to reduce costs while improving sustainability?
Read our blog post on strategies to optimize supply chain costs »
Circular Supply Chains in Action: The Role of Lynksols
Lynksols supports circular supply chain principles through its innovative reusable straps – the StrapPRO® – a smart alternative to single-use plastic wraps and straps traditionally used in pallet logistics. Instead of contributing to waste and inefficiency, Lynksols’ strap system is designed for durability, safety, and repeated use. These solutions help businesses reduce environmental impact while improving operational efficiency.
Key benefits of StrapPRO® include:
Reduction of single-use plastics: Replaces disposable plastic films, minimizing landfill waste.
Extended lifespan: Each strap is engineered for hundreds to thousands of reuse cycles, depending on the model.
Cost-efficiency: Long-term savings by eliminating recurring purchases of disposable materials.
Carbon footprint reduction: Less waste generation and more efficient use of resources throughout the supply chain.
Increased safety and consistency: Designed to meet varying operational demands, from light-duty to critical logistics.
By integrating Lynksols’ StrapPRO® reusable straps into their logistics operations, companies not only lower costs but also advance their sustainability goals by embracing a more circular, eco-conscious approach to packaging and transport.



